DiSSCo Core Architecture
Before we can delve into how MASs connect to the DiSSCo architecture, it is useful to know how the DiSSCo architecture operates.
As a platform, DiSSCo sits in between data providers and data consumers. The core architecture adds value by harmonizing data to openDS, minting unique identifiers for specimens and media objects, capturing provenance, and, of course, facilitating annotations. As DiSSCo improves the data, DiSSCo will send this enhanced data upstream, back to the data providers, and downstream, to data aggregators (though this functionality is currently in development).
Due to its flexible nature, additional services can be built on top of the DiSSCo core architecture. A MAS is one such service. What a MAS does is essentially a “black box” from the DiSSCo Architecture’s perspective. A MAS receives a message as input and produces an annotation as an output.
The DiSSCo position in the biodiversity data landscape is illustrated in the following diagram. On the left, data providers send data to the core infrastructure. In the middle, machine and human agents rest on top of the core infrastructure, adding additional value. On the right, the enriched data is sent to data consumers.
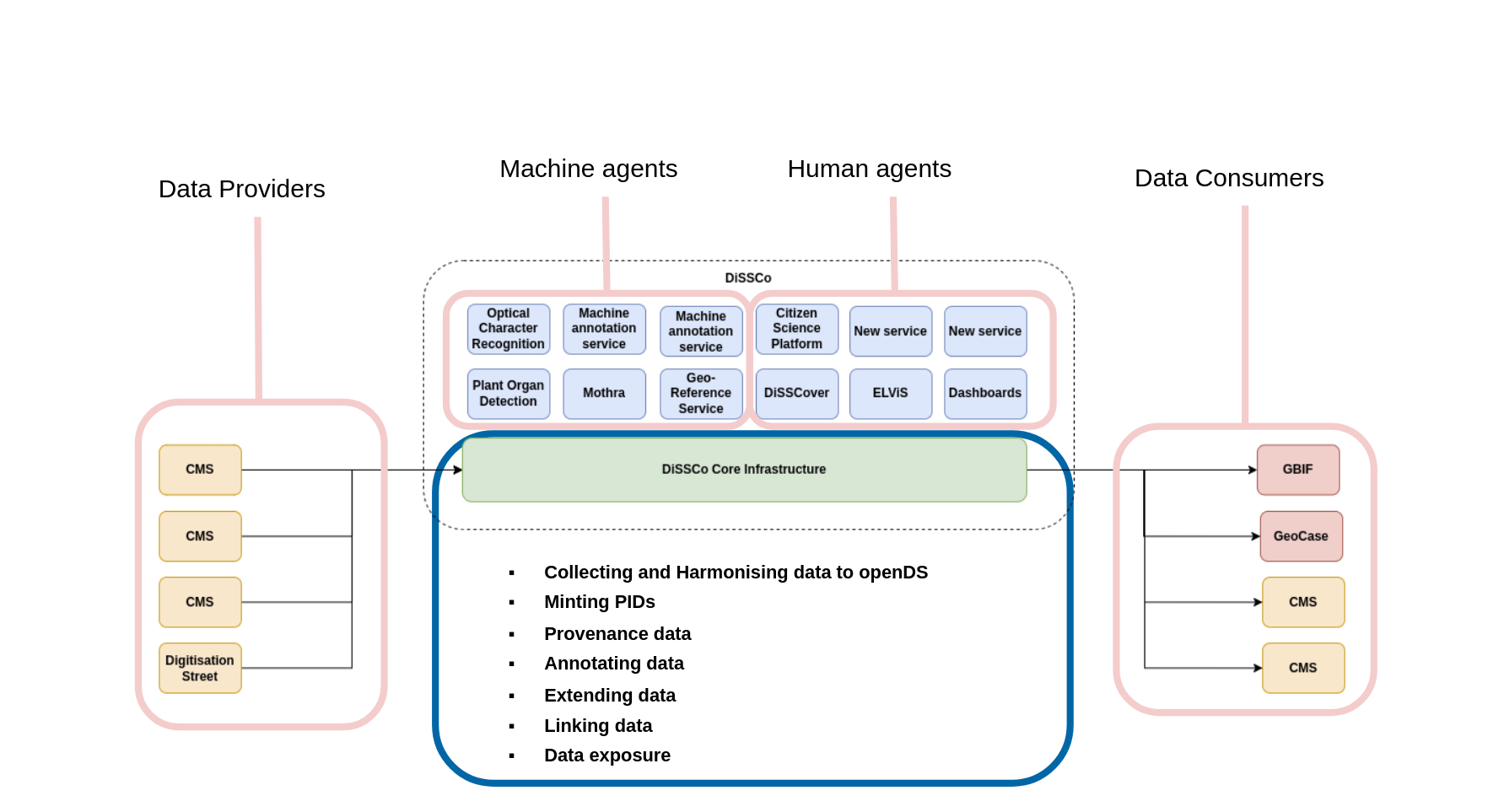
Other value services of DiSSCo:
- Harmonising data to OpenDS
- Minting Persistent Identifiers (PIDs) for resources
- Versioning objects and maintaining a provenance record
- Extending data and linking
- Exposing data through APIs, including a robust search function
Machine Annotation Services
A Machine Annotation Service (MAS) is an automated service that annotates a target in DiSSCo. Most often, MASs are scheduled by a user on a specific target - either a digital specimen or a media object – either through the DiSSCover platform or programmatically through the DiSSCo API.
When an existing service is adapted to work within DiSSCo, there are two components involved:
- Value Service: This is the original service being adapted to DiSSCo. It is deployed on infrastructure separate from the core DiSSCo architecture, and should be accessible through APIs.
- MAS Middleware: This is a lightweight component containerized and deployed on the DiSSCo core architecture.
When a machine makes an annotation
The flow of data can be summarised below:
1. The user requests a job
Through the DiSSCover platform, a user schedules a MAS on a specific target. DiSSCover calls the DiSSCo backend to schedule a job.
2. The backend sends a message
DiSSCo uses Apache Kafka as an asynchronous messaging service. When a machine annotation is requested, a “job” is created. A UUID is generated and associated with this process to track the state of the job. When it is first created, the job is marked as SCHEDULED.
The backend sends a message through Kafka. This message that includes the job ID and the target of the annotation. The message has a topic that identifies the message’s destination. Each MAS is given its own unique topic by DiSSCo.
3. The job is received by the MAS middleware
Listening for a Kafka message on its topic, the MAS receives the message.
3a. (Recommended) The MAS middleware informs the backend the job was received.
It is strongly recommended that once the MAS receives the message, it informs the backend. This improves user experience. The MAS sends the job id to the /running endpoint. The backend, in turn, marks the job as RUNNING and informs the user.
4. The MAS middleware calls the value service The MAS middleware extracts relevant information from the target and sends it to the value service, usually through an API call. The results from the value service are formatted into an annotation event.
5. The results are sent to DiSSCo The MAS middelware sends the formatted annotation event through the annotation Kafka topic.
6. The annotation is processed DiSSCo’s annotation processing service picks up the message in the annotation topic and processes it. The annotation is then available through the DiSSCo API and the DiSSCover interface.
Congratulations! You’ve annotated an object!
MAS Deployment
The MAS middleware application is deployed as a container on the DiSSCo core architecture. The value service will remain deployed where it was originally.
The MAS middleware is deployed on the DiSSCo network. If your value service requires whitelisting a specific IP address, let the DiSSCo team know so they can provide your MAS middleware with a static IP address. That way, the middleware may communicate with the value service.